PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Stable under ordinary conditions (Hygroscopic)
APPLICATIONS
Sulfonic acid is acidic due to the hydrogen atom, stronger than a carboxylic acid. Sulfonic acid is one of the most important organo sulfur compounds in organic synthesis. Sulfonic acids are used as catalysts in esterification, alkylation and condensation reactions. Sulfonates are salts or esters of sulfonic acid. Sulfonic salts are soluble in water. Sulfonic acid and its salts present in organic dyes provide useful function of water solubility and or improve the washfastness of dyes due to their capabiltity of binding more tightly to the fabric.
They are widely used in the detergent industry. Alkylbenzene sulfonic acid is the largest-volume synthetic surfactant because of its relatively low cost, good performance, the fact that it can be dried to a stable powder and the biodegradable environmental friendliness. Sulfonate cleaners do not form an insoluble precipitates in hard water. Sulfonic acid salts and esters are intermediates widely used in organic synthesis and particularly phenolic compounds and cation exchange resins. They are synthetic intermediates for a number of biologically active compounds and pharmaceutical candidates such as sulfa drugs.
Benzenesulfonic acid consumption is linked mostly to phenol and resorcinol production with sodium hydroxide. It is used as a catalyst for dehydration and used in solidifying resins. It is a base material for electroplating solutions. Benzenesulfonic acid, or a derivative thereof, is used as a synthetic intermediate for a number of chemical families of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, dyes, pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and other organic compounds. Commercially, benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt is more common due to high deliquescence of the base material.
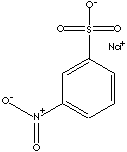
3-Nitrobenzenesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt is used as an intermediate for dyes and fluorescent brightening agent. It is used as an developing agent for electroplating and auxiliary for dying fabrics.
APPEARANCE
PURITY
96.0% min
- Michael addition
- Reduction
- Henry Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion reaction
- Alkylation, Acylation, and Halogenation
PRICE
INFORMATION